MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
(no entry for this year)
1810
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1811
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1812
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1813
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Francisco de Goya: The Third of May 1808 (also known as El tres de mayo de 1808 en Madrid or Los fusilamientos de la montaña del Príncipe Pío, or Los fusilamientos del tres de mayo) is now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. In the work, Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the occupation of 1808 in the Peninsular War. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. The painting's content, presentation, and emotional force secure its status as a groundbreaking, archetypal image of the horrors of war. Although it draws on many sources from both high and popular art, The Third of May 1808 marks a clear break from convention. Diverging from the traditions of Christian art and traditional depictions of war, it has no distinct precedent, and is acknowledged as one of the first paintings of the modern era. According to the art historian Kenneth Clark, The Third of May 1808 is "the first great picture which can be called revolutionary in every sense of the word, in style, in subject, and in intention".
Painting by Francisco de Goya: The Third of May 1808 (also known as El tres de mayo de 1808 en Madrid or Los fusilamientos de la montaña del Príncipe Pío, or Los fusilamientos del tres de mayo) is now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. In the work, Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the occupation of 1808 in the Peninsular War. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. The painting's content, presentation, and emotional force secure its status as a groundbreaking, archetypal image of the horrors of war. Although it draws on many sources from both high and popular art, The Third of May 1808 marks a clear break from convention. Diverging from the traditions of Christian art and traditional depictions of war, it has no distinct precedent, and is acknowledged as one of the first paintings of the modern era. According to the art historian Kenneth Clark, The Third of May 1808 is "the first great picture which can be called revolutionary in every sense of the word, in style, in subject, and in intention".
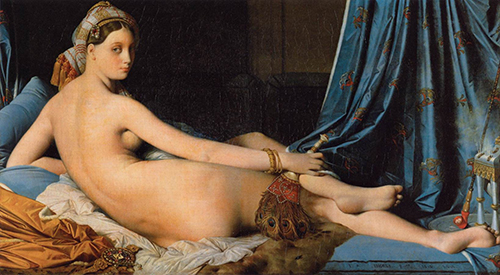 Painting by Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres: Grande Odalisque, also known as Une Odalisque or La Grande Odalisque depicts an odalisque, or concubine. Ingres' contemporaries considered the work to signify Ingres' break from Neoclassicism, indicating a shift toward exotic Romanticism. Grande Odalisque attracted wide criticism when it was first shown. It has been especially noted for the elongated proportions and lack of anatomical realism. The work is displayed in the Louvre, Paris. The painting was commissioned by Napoleon's sister, Queen Caroline Murat of Naples, and finished in 1814. Ingres drew upon works such as Dresden Venus by Giorgione, and Titian's Venus of Urbino as inspiration for his reclining nude figure, though the actual pose of a reclining figure looking back over her shoulder is directly drawn from the 1809 Portrait of Madame Récamier by Jacques-Louis David. Madame Récamier painted by Jacques-Louis David (1800). Ingres portrays a concubine in languid pose as seen from behind with distorted proportions. The small head, elongated limbs, and cool color scheme all reveal influences from Mannerists such as Parmigianino, whose Madonna with the Long Neck was also famous for anatomical distortion. This eclectic mix of styles, combining classical form with Romantic themes, prompted harsh criticism when it was first shown in 1814. Critics viewed Ingres as a rebel against the contemporary style of form and content
Painting by Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres: Grande Odalisque, also known as Une Odalisque or La Grande Odalisque depicts an odalisque, or concubine. Ingres' contemporaries considered the work to signify Ingres' break from Neoclassicism, indicating a shift toward exotic Romanticism. Grande Odalisque attracted wide criticism when it was first shown. It has been especially noted for the elongated proportions and lack of anatomical realism. The work is displayed in the Louvre, Paris. The painting was commissioned by Napoleon's sister, Queen Caroline Murat of Naples, and finished in 1814. Ingres drew upon works such as Dresden Venus by Giorgione, and Titian's Venus of Urbino as inspiration for his reclining nude figure, though the actual pose of a reclining figure looking back over her shoulder is directly drawn from the 1809 Portrait of Madame Récamier by Jacques-Louis David. Madame Récamier painted by Jacques-Louis David (1800). Ingres portrays a concubine in languid pose as seen from behind with distorted proportions. The small head, elongated limbs, and cool color scheme all reveal influences from Mannerists such as Parmigianino, whose Madonna with the Long Neck was also famous for anatomical distortion. This eclectic mix of styles, combining classical form with Romantic themes, prompted harsh criticism when it was first shown in 1814. Critics viewed Ingres as a rebel against the contemporary style of form and content
1814
 Painting by Francisco de Goya: The Third of May 1808 (also known as El tres de mayo de 1808 en Madrid or Los fusilamientos de la montaña del Príncipe Pío, or Los fusilamientos del tres de mayo) is now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. In the work, Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the occupation of 1808 in the Peninsular War. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. The painting's content, presentation, and emotional force secure its status as a groundbreaking, archetypal image of the horrors of war. Although it draws on many sources from both high and popular art, The Third of May 1808 marks a clear break from convention. Diverging from the traditions of Christian art and traditional depictions of war, it has no distinct precedent, and is acknowledged as one of the first paintings of the modern era. According to the art historian Kenneth Clark, The Third of May 1808 is "the first great picture which can be called revolutionary in every sense of the word, in style, in subject, and in intention".
Painting by Francisco de Goya: The Third of May 1808 (also known as El tres de mayo de 1808 en Madrid or Los fusilamientos de la montaña del Príncipe Pío, or Los fusilamientos del tres de mayo) is now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. In the work, Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the occupation of 1808 in the Peninsular War. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. The painting's content, presentation, and emotional force secure its status as a groundbreaking, archetypal image of the horrors of war. Although it draws on many sources from both high and popular art, The Third of May 1808 marks a clear break from convention. Diverging from the traditions of Christian art and traditional depictions of war, it has no distinct precedent, and is acknowledged as one of the first paintings of the modern era. According to the art historian Kenneth Clark, The Third of May 1808 is "the first great picture which can be called revolutionary in every sense of the word, in style, in subject, and in intention".
 Painting by Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres: Grande Odalisque, also known as Une Odalisque or La Grande Odalisque depicts an odalisque, or concubine. Ingres' contemporaries considered the work to signify Ingres' break from Neoclassicism, indicating a shift toward exotic Romanticism. Grande Odalisque attracted wide criticism when it was first shown. It has been especially noted for the elongated proportions and lack of anatomical realism. The work is displayed in the Louvre, Paris. The painting was commissioned by Napoleon's sister, Queen Caroline Murat of Naples, and finished in 1814. Ingres drew upon works such as Dresden Venus by Giorgione, and Titian's Venus of Urbino as inspiration for his reclining nude figure, though the actual pose of a reclining figure looking back over her shoulder is directly drawn from the 1809 Portrait of Madame Récamier by Jacques-Louis David. Madame Récamier painted by Jacques-Louis David (1800). Ingres portrays a concubine in languid pose as seen from behind with distorted proportions. The small head, elongated limbs, and cool color scheme all reveal influences from Mannerists such as Parmigianino, whose Madonna with the Long Neck was also famous for anatomical distortion. This eclectic mix of styles, combining classical form with Romantic themes, prompted harsh criticism when it was first shown in 1814. Critics viewed Ingres as a rebel against the contemporary style of form and content
Painting by Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres: Grande Odalisque, also known as Une Odalisque or La Grande Odalisque depicts an odalisque, or concubine. Ingres' contemporaries considered the work to signify Ingres' break from Neoclassicism, indicating a shift toward exotic Romanticism. Grande Odalisque attracted wide criticism when it was first shown. It has been especially noted for the elongated proportions and lack of anatomical realism. The work is displayed in the Louvre, Paris. The painting was commissioned by Napoleon's sister, Queen Caroline Murat of Naples, and finished in 1814. Ingres drew upon works such as Dresden Venus by Giorgione, and Titian's Venus of Urbino as inspiration for his reclining nude figure, though the actual pose of a reclining figure looking back over her shoulder is directly drawn from the 1809 Portrait of Madame Récamier by Jacques-Louis David. Madame Récamier painted by Jacques-Louis David (1800). Ingres portrays a concubine in languid pose as seen from behind with distorted proportions. The small head, elongated limbs, and cool color scheme all reveal influences from Mannerists such as Parmigianino, whose Madonna with the Long Neck was also famous for anatomical distortion. This eclectic mix of styles, combining classical form with Romantic themes, prompted harsh criticism when it was first shown in 1814. Critics viewed Ingres as a rebel against the contemporary style of form and content
(no entry for this year)
1815
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1816
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1817
(no entry for this year)
 painting by Caspar David Friedrich: Wanderer above the Sea of Fog (German: Der Wanderer über dem Nebelmeer), also known as Wanderer Above the Mist or Mountaineer in a misty Landscape, currently resides in the Kunsthalle Hamburg in Hamburg, Germany. Wanderer above the Sea of Fog is true to the Romantic style and Friedrich's style in particular. Gorra's (2004) analysis was that the message conveyed by the painting is one of Kantian self-reflection, expressed through the wanderer's gazings into the murkiness of the sea of fog.
painting by Caspar David Friedrich: Wanderer above the Sea of Fog (German: Der Wanderer über dem Nebelmeer), also known as Wanderer Above the Mist or Mountaineer in a misty Landscape, currently resides in the Kunsthalle Hamburg in Hamburg, Germany. Wanderer above the Sea of Fog is true to the Romantic style and Friedrich's style in particular. Gorra's (2004) analysis was that the message conveyed by the painting is one of Kantian self-reflection, expressed through the wanderer's gazings into the murkiness of the sea of fog.
1818
 painting by Caspar David Friedrich: Wanderer above the Sea of Fog (German: Der Wanderer über dem Nebelmeer), also known as Wanderer Above the Mist or Mountaineer in a misty Landscape, currently resides in the Kunsthalle Hamburg in Hamburg, Germany. Wanderer above the Sea of Fog is true to the Romantic style and Friedrich's style in particular. Gorra's (2004) analysis was that the message conveyed by the painting is one of Kantian self-reflection, expressed through the wanderer's gazings into the murkiness of the sea of fog.
painting by Caspar David Friedrich: Wanderer above the Sea of Fog (German: Der Wanderer über dem Nebelmeer), also known as Wanderer Above the Mist or Mountaineer in a misty Landscape, currently resides in the Kunsthalle Hamburg in Hamburg, Germany. Wanderer above the Sea of Fog is true to the Romantic style and Friedrich's style in particular. Gorra's (2004) analysis was that the message conveyed by the painting is one of Kantian self-reflection, expressed through the wanderer's gazings into the murkiness of the sea of fog.
 Painting by Théodore Géricault: The Raft of the Medusa (French: Le Radeau de la Méduse) was completed when the artist was 27. The work has become an icon of French Romanticism. At 16' 1" × 23' 6", it is an over-life-size painting that depicts a moment from the aftermath of the wreck of the French naval frigate Méduse, which ran aground off the coast of today's Mauritania on 2 July 1816. On 5 July 1816, at least 147 people were set adrift on a hurriedly constructed raft; all but 15 died in the 13 days before their rescue, and those who survived endured starvation and dehydration and practised cannibalism. Géricault chose to depict this event in order to launch his career with a large-scale uncommissioned work on a subject that had already generated great public interest. The event fascinated him, and before he began work on the final painting, he undertook extensive research and produced many preparatory sketches. He interviewed two of the survivors and constructed a detailed scale model of the raft. He visited hospitals and morgues where he could view, first-hand, the colour and texture of the flesh of the dying and dead. As he had anticipated, the painting proved highly controversial at its first appearance in the 1819 Paris Salon, attracting passionate praise and condemnation in equal measure. However, it established his international reputation, and today is widely seen as seminal in the early history of the Romantic movement in French painting.
Painting by Théodore Géricault: The Raft of the Medusa (French: Le Radeau de la Méduse) was completed when the artist was 27. The work has become an icon of French Romanticism. At 16' 1" × 23' 6", it is an over-life-size painting that depicts a moment from the aftermath of the wreck of the French naval frigate Méduse, which ran aground off the coast of today's Mauritania on 2 July 1816. On 5 July 1816, at least 147 people were set adrift on a hurriedly constructed raft; all but 15 died in the 13 days before their rescue, and those who survived endured starvation and dehydration and practised cannibalism. Géricault chose to depict this event in order to launch his career with a large-scale uncommissioned work on a subject that had already generated great public interest. The event fascinated him, and before he began work on the final painting, he undertook extensive research and produced many preparatory sketches. He interviewed two of the survivors and constructed a detailed scale model of the raft. He visited hospitals and morgues where he could view, first-hand, the colour and texture of the flesh of the dying and dead. As he had anticipated, the painting proved highly controversial at its first appearance in the 1819 Paris Salon, attracting passionate praise and condemnation in equal measure. However, it established his international reputation, and today is widely seen as seminal in the early history of the Romantic movement in French painting.
1819
 Painting by Théodore Géricault: The Raft of the Medusa (French: Le Radeau de la Méduse) was completed when the artist was 27. The work has become an icon of French Romanticism. At 16' 1" × 23' 6", it is an over-life-size painting that depicts a moment from the aftermath of the wreck of the French naval frigate Méduse, which ran aground off the coast of today's Mauritania on 2 July 1816. On 5 July 1816, at least 147 people were set adrift on a hurriedly constructed raft; all but 15 died in the 13 days before their rescue, and those who survived endured starvation and dehydration and practised cannibalism. Géricault chose to depict this event in order to launch his career with a large-scale uncommissioned work on a subject that had already generated great public interest. The event fascinated him, and before he began work on the final painting, he undertook extensive research and produced many preparatory sketches. He interviewed two of the survivors and constructed a detailed scale model of the raft. He visited hospitals and morgues where he could view, first-hand, the colour and texture of the flesh of the dying and dead. As he had anticipated, the painting proved highly controversial at its first appearance in the 1819 Paris Salon, attracting passionate praise and condemnation in equal measure. However, it established his international reputation, and today is widely seen as seminal in the early history of the Romantic movement in French painting.
Painting by Théodore Géricault: The Raft of the Medusa (French: Le Radeau de la Méduse) was completed when the artist was 27. The work has become an icon of French Romanticism. At 16' 1" × 23' 6", it is an over-life-size painting that depicts a moment from the aftermath of the wreck of the French naval frigate Méduse, which ran aground off the coast of today's Mauritania on 2 July 1816. On 5 July 1816, at least 147 people were set adrift on a hurriedly constructed raft; all but 15 died in the 13 days before their rescue, and those who survived endured starvation and dehydration and practised cannibalism. Géricault chose to depict this event in order to launch his career with a large-scale uncommissioned work on a subject that had already generated great public interest. The event fascinated him, and before he began work on the final painting, he undertook extensive research and produced many preparatory sketches. He interviewed two of the survivors and constructed a detailed scale model of the raft. He visited hospitals and morgues where he could view, first-hand, the colour and texture of the flesh of the dying and dead. As he had anticipated, the painting proved highly controversial at its first appearance in the 1819 Paris Salon, attracting passionate praise and condemnation in equal measure. However, it established his international reputation, and today is widely seen as seminal in the early history of the Romantic movement in French painting.
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.